Why UTC?
UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) is used as the basic time zone in myDatanet. This applies both to the server itself and to all data loggers communicating with the server.
The reason behind this is simply explained: All time zones available in the world are based on UTC. All local times can be calculated by specifying the time zone and the additional specification of summer and winter time.
In the opposite direction, this is not possible every second of the year. With Central European Summer Time, there is a changeover from UTC+2 (summer time) to UTC+1 (standard time, “winter time”) every last Sunday in October. Commonly, the time is “set back” from 03:00 to 02:00, so the hour from 02:00 to 03:00 exists twice in a row. Technically, storage in local time would not be feasible or only with unjustifiable complexity.
This is how it works with time in myDatanet
In the myDatanet ecosystem, timestamps can be stored or captured in a 1/256 second grid. It is therefore not possible to capture data records for every single millisecond. The timestamps are always spaced 1/256 seconds apart, which is exactly 3.90625 milliseconds. This value is always rounded to whole milliseconds internally. Therefore, intervals of 3 or 4 milliseconds result here, depending on which exact value is currently used.
Where does the server get the current time from?
The current date and time are obtained by the myDatanet server directly from the underlying operating system. The updating of the time on the operating system can be taken over on the one hand by the operating system itself (if configured) or by myDatanet (adjustable, synchronization with public time servers via NTP).
Synchronization with data loggers
When establishing the connection from a device to the server, the current timestamp (UTC) is transferred from the server to the device. The device adopts the transmitted timestamp as the new time. If the time in the device is corrected by more than 5 seconds, a corresponding entry is written in the device log.
The local time in the device
Each device also receives information from the server about the time zone in which it actually operates. Which time zone is used is determined in this order: Site -> Client -> Server . If no specific setting has been made in the site, the customer’s settings will be applied. If there is no specific setting there either, the settings of the server are used.
Example: When using daily counters, it is important to reset the counter at the correct time. To do this, it must also be possible to correctly interpret the time set for resetting on the device. However, the storage of the recorded data is still in UTC.
Configurations and historical data sets
The synchronization of the data loggers with the server is primarily controlled via timestamps. At the beginning of each connection, the device reports to the server the current timestamp (for “single” data sets such as configurations) or the latest timestamp (for historical data streams) for each individual data block or historical data stream.
In addition, the direction in which configurations may be synchronized is taken into account. For IoT apps, this can be defined by the app developer. It makes sense to synchronize settings in one direction only, e.g. “config2” only upload, “config3” only download. This allows any discrepancies to be prevented at the time of development.
If the timestamp on the device is newer, the server requests the new data from the device. If the timestamp on the server is newer, the server sends the changed record to the device.
Synchronization of files
The synchronization of files follows a similar pattern as the configurations. If a file can be transferred in both directions, the version with the older timestamp is always overwritten.
However, the synchronization logic of files includes other criteria that come into play before the timestamp. Depending on the design of the respective application, files are usually only transferred unidirectionally or not at all.
It is recommended to separate files between upload and download and not to let the same file be transferred in both directions.
User settings
The display of clock times can be configured on several levels on the server. The settings are handled in the following order: User -> Site -> Customer -> Server .
User level
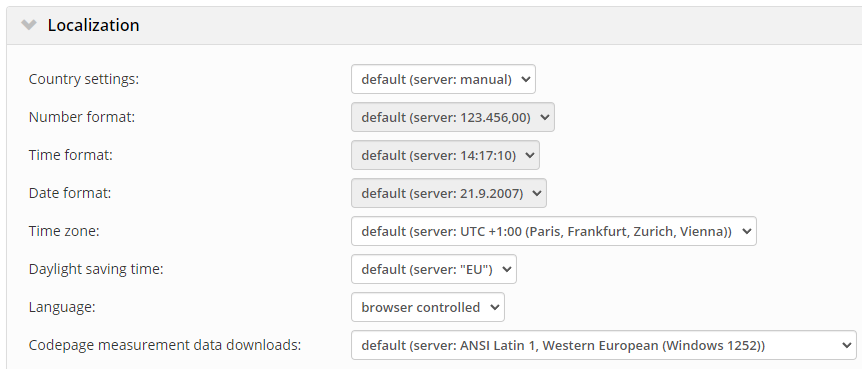
If the localization settings are changed at the user level, then all timestamps on the server will be displayed in that time zone, regardless of any other site, client, or server settings.
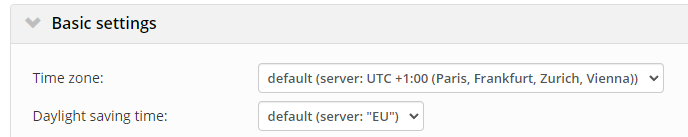
Site level
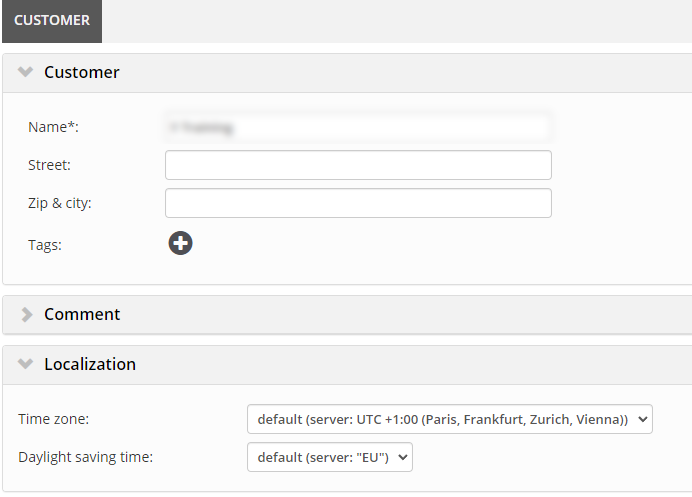
Customer level
Server level
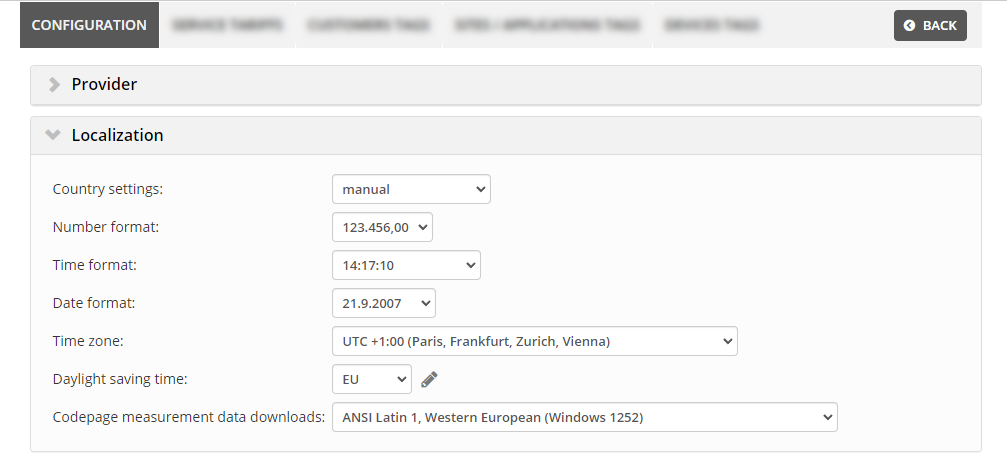
Server administrators can set the default settings for displaying timestamps on the server.
How it works in the REST API
The timestamps issued by the REST API or received as parameters are always traded in standard time UTC, except it is explicitly described otherwise in the individual resource.
However, the use of local time is rarely found in the REST API and is only used when a reference to local time becomes necessary. An example of this is the condensed output of measured values, which are output in daily intervals or even larger intervals. The calculation of values like minimum, maximum, average etc. is only useful if the data is displayed in local time. The same applies to daily totals, which are usually reset at midnight of the local time zone.


