The industry has increasingly recognised the advantages of remotely networked products. Large fleets of devices are monitored over a long product lifetime. The sensors, devices or machines are often distributed in many countries, and the place of use is sometimes unknown or difficult to access.
The management and maintenance of the devices and machines thus becomes a challenge. While this topic is often mentally postponed at the beginning, there is an urgent need for action at the latest 5 to 7 years after commissioning.
Device management is also indispensable with regard to scaling the business model. At the latest when the devices can no longer be managed clearly with the often popular Excel list or the magic 100 piece mark is reached, you will appreciate the value of a device management.
What is device management?
Device management offers the responsible teams secure control and monitoring of remotely operated sensors, device and machine fleets.
Comparable to Mobile Device Management (MDM), as it is known for smartphones in the IT infrastructure, end devices are securely managed in the life cycle.
The functions of a device management support with:
- Automated picking processes
- Commissioning
- Operational operation and administration
What are the benefits of device management?
The advantage is not only a comfortable and secure device fleet, but also transparency about the overall status of all objects, fast response times, shorter support times and a high-quality service for users and operators.
The most important benefits
Control and transparency reduces risks
- Management via weblogin (single point of service)
- Status display with integrated analysis functions of the entire infrastructure
- Automated process chains or direct manual intervention
Security is a continuous process
- Version and compatibility management of hardware and software
- Predefined configurations reduce operating errors
- Fully integrated remote updates of devices in operation
- Persistent configuration storage for individual unit settings
Competence and efficiency
- Fast response times with expert availability in case of support
- Efficient aftercare and configuration adjustment
- Secure scaling through highly automated processes
The Digital Device ID is the basis for Device Management
The basis for device management is the underlying identification architecture, which ensures security and flexibility in the life cycle. Device ID management is used for this.
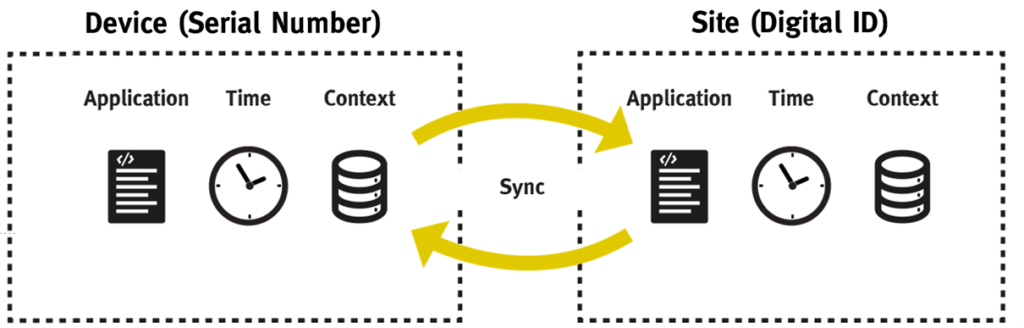
The digital identity is a combination of the physical device (hardware and firmware), here the Device Serial Number, and the site (the digital image), here Digital ID.
This abstraction facilitates picking processes and allows automation. This enables continuous management from the start of the product directly at its creation, through picking, exchange, configuration management and security. Compatibility and context are checked systemically in order to connect the identities securely. You can find out more about this in the Security Whitepaper.
The exchange process is established by means of synchronisation, whereby the remote update function is a central component.
Remote Update is a deeply integrated basic function and not an add-on
The update function of a distributed network is the reinsurance for unforeseeable problem cases and allows a much higher flexibility and speed in product development. Modern products with a high focus on analysis are sometimes only finally developed in “live operation”. Examples include Artificial Neuronal Networks (ANN) of autonomous vehicles or Machine Learning (ML) applications in industry.
In practice, remote updates are processed manually or automatically. The updates can, for example, be prevented “Off”, automatically applied “On” or applied once “Once”. The firmware of the rapidM2M stack is automatically available in the cloud:
- Beta Release
- Release Canditate
- Released
Compatible versions are displayed with the version information in the administration. The update process is fully automated, repetition and status are displayed.
In the development studio rapidM2M Studio, the version levels and hardware compatibility are defined in the project settings. The application context of the application is commissioned manually using an IoT app or managed, distributed and installed automatically using application management. In the process, firmware and application can be played out automatically via device fleets. The update process is handled according to the configuration. In the application part, a distinction is made between the following statuses:
- In development without device synchronisation
- In development with bidirectional device synchronisation
- Productive – device status is overridden
Applications can be created very comfortably online with one of the most modern and consistent development tools, the rapidM2M Studio. Registration is free of charge.
On-Demand Demo
Fast and easy IoT development.
Get to know the rapidM2M Studio in 20 minutes.
How does a device appear in the management interface during commissioning?
Activation is established by means of simple serial number activation. For this purpose, the first automated pre-provisioning process already takes place in the background in production in order to be available for the simple or automated device activation.
For the user, the last step of activation is very convenient and is triggered automatically during commissioning. This is done either via an automatic mechanism (e.g. Microtronics Registration App) or manually in the Device Management interface.
In this step, the device serial number is linked to the digital site. The physical device thus receives the final commissioning, whereby the last or current software status can also be inherited at the first connection or login.
What does the Device Management user interface look like?
Online via web browser, the Device Management Portal provides a comprehensive range of functions. Device Management is extended in the professional service offerings with cross-customer functions to manage the entire product fleet or individual device versions, device types to all customers or for specific customers.
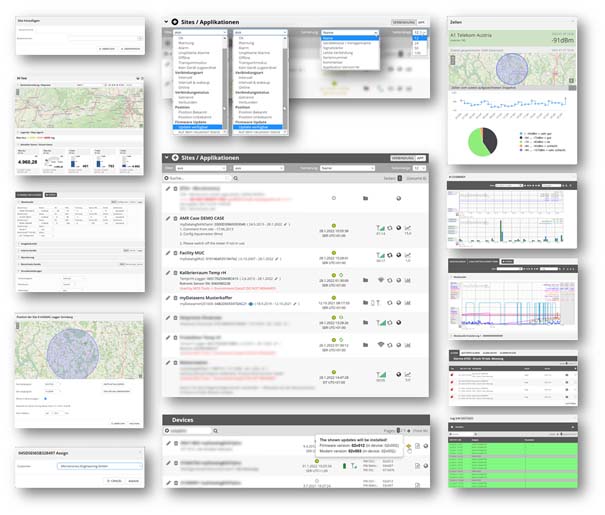
The compact list view (centre of the picture) is the heart of the Device Management Portal. It shows all relevant information about the devices. The list view contains a wealth of information, the depth of which cannot even be guessed at first.
- Name of the device, which is assigned manually or automatically in the course of commissioning. For later identification, the location, purpose, meter number or serial number can be used as a name.
- IoT app used as a template for the digital device software twin. The IoT app model represents the context, the data model and the application logic.
- Automatically or manually assigned device serial number.
- Date range of continuous data storage (from to).
- Device status(Unassigned, Assigned, Offline, OK, Online, Synchronisation, Warning, Alarm).
- Time of last data synchronisation with upload/download statistics
- File browser for application file synchronisation (upload or download files between unit and site)
- Battery status indication (if available in the application)
- Connection status indication with bars or status depending on the technology (mobile radio, WiFi, LAN, etc.) with extensive analysis of the connection quality and the network connection (picture top right Mobile radio quality analysis). In the case of cyclically operating battery-powered devices, the time until the next connection to the remote device.
- Wakeup or adhoc remote synchronisation to offline devices if supported and configured by the device. Read more about connection types here.
- Location display or installation location with display by means of a circle or pin depending on the technology used (e.g. mobile cell location, heat mapping, GNSS location). The location is dynamic or fixed depending on the application.
- Raw data browser or predefined dashboard for quick analysis and overview of the current congestion and the historical course.
- Location pin when using the dynamic overview map or graphical application mapping.
But the list view is only the heart of device management. Many veins take us to widely ramified functions. Here is Here is a selection of further relevant features:
- User authorisation levels distinguish administrative and operationally relevant functional roles.
- Adding, changing and deleting manual creation and editing
- Site management for picking physical device identifications with the digital twin. The full range of functions is only offered at the higher administration level.
- Manual serial number allocation via a device pool for preparation or intermediate commissioning with allocation functions in a device fleet or also the change to new customer accounts for service and rental devices. Manual commissioning in use of rental equipment fleets or service equipment with continuous calibration cycle.
- Unit software: version status and update option
- Device log file with simple and detailed display of status, processes and error codes
- Extensive filtering, filter combinations and sorting (see picture in the middle above)
- Tagging expands filtering options such as grouping, combinations, exclusion
- Search with term storage of the last search and advanced search with various options
- A large number of managed devices requires practical retrieval using intelligent filters and well-structured tags.
- Batch processing or automated processes for fleet management are offered via application management.
- The availability of the entire fleet status is displayed in the health dashboard via real-time analysis.
Conclusion
Device management offers much more than just an overview of the devices. It is your control and administration centre in daily work with remotely networked sensors, devices and machines.
In addition to the advantages of device management per se, this article has given you an insight into the diverse functionalities. Depending on the tariff and configuration, these are available to you. Make an appointment for a free 30-minute demonstration. Take the opportunity to ask all your questions and evaluate device management for your business case.